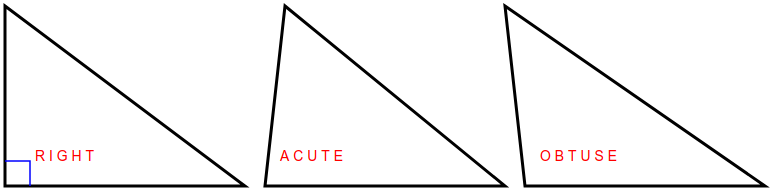
Triangle is called right when one of its three angles is right angle, equal to 90° - i.e. sides of this angle are orthogonal.
Such triangles are important since for them the Pythagorean Theorem works. Let's recollect it.
Sides, adjacent to the right angle of such triangle, are called legs and the third side is hypotenuse. The theorem states that length of hypotenuse is determined by the lengths of legs with simple formula:
c^2 = a^2 + b^2
or
c = sqrt(a^2 + b^2)
Where c is the length of hypotenuse, while a and b are lengths of legs.
Famous example of the right triangle is one with sides of 3, 4 and 5 units. Really, for them theorem holds:
5^2 = 3^2 + 4^2
or
25 = 9 + 16
In this task you will use this theorem to write a program which could determine, whether the triangle is right, or it is acute, or obtuse:
- for acute triangle its longest side is shorter than hypotenuse should be;
- for obtuse triangle its longest side is longer than hypotenuse should be.
Input data contains the number of triangles in the first line.
Next lines describe one triangle each. Descriptions consist of three values - lengths of sides. Largest value would
always be the last of three for simplicity.
Answers should have one of the letters R (right), A (acute) or O (obtuse) for each of triangles. Letters
should be separated by spaces.
Example:
input data:
3
6 8 9
9 12 15
16 12 22
answer:
A R O